1980 Pontiac LeMans Station Wagon - G-T-faux (stuck with it, and can't shake it... like a bad case of herpes)
- Thread starter motorheadmike
- Start date
You are using an out of date browser. It may not display this or other websites correctly.
You should upgrade or use an alternative browser.
You should upgrade or use an alternative browser.
- Status
- Not open for further replies.
You gonna use the gold, spacey stuff?
Yup! Going to call it my "gol' toof".
Ordered 120 meters of it. LOL!
Took the day off work so I could trim, sand, prime, and paint this "thing".
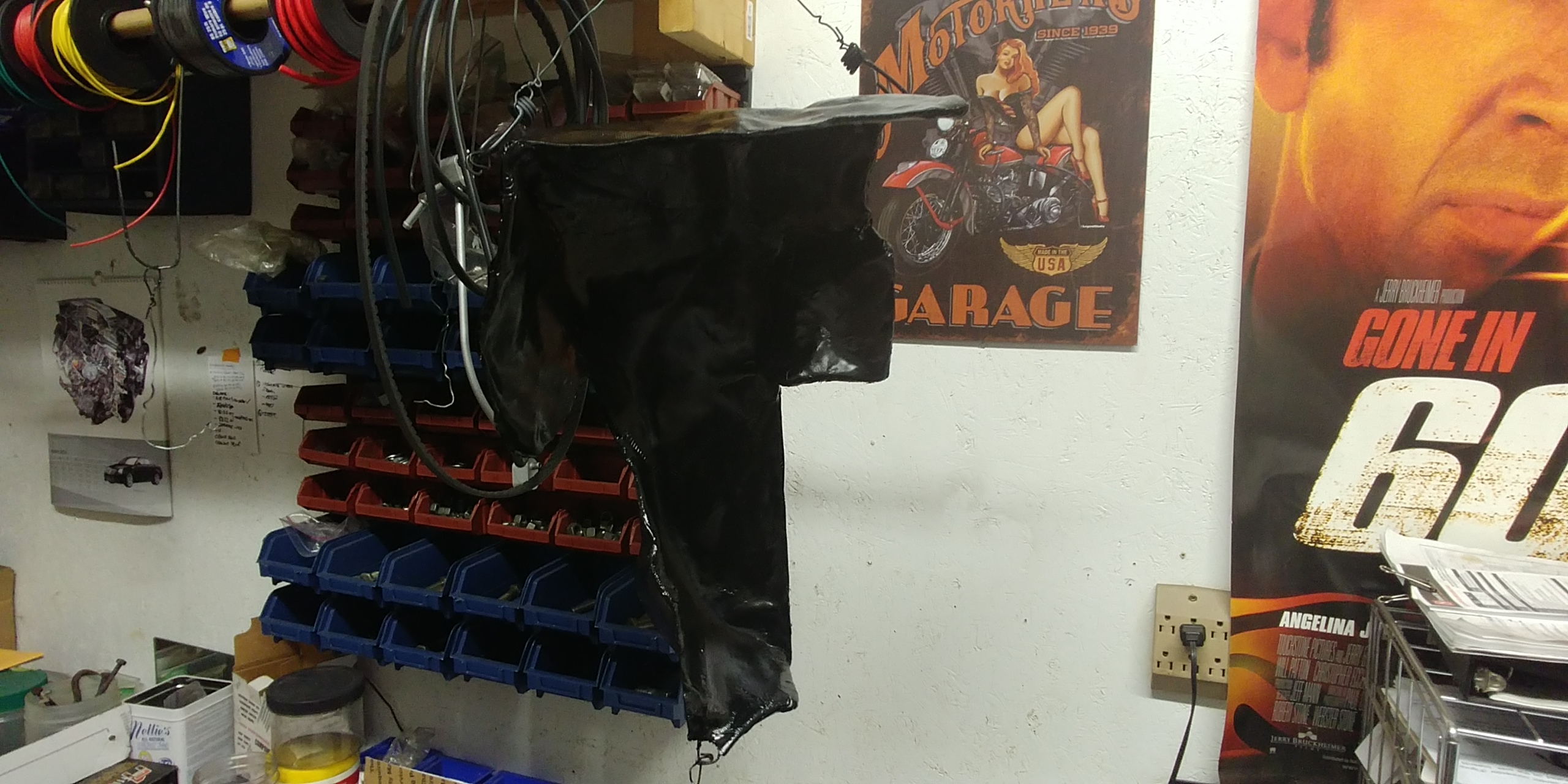

I used epoxy-based primer and paint as a best guess of what wouldn't have a negative reaction to Bondo's "proprietary resin" (a trade secret blend of 11 herbs and spices according to the can) - it was that or assume it was polymer resin and used polymer-based paint. I stand by my decision - plus epoxy paint is a little more resistant to solvents and chemicals.
I'll install it tomorrow with some temporary foam insulation - then we wait for China to do it's part.

I used epoxy-based primer and paint as a best guess of what wouldn't have a negative reaction to Bondo's "proprietary resin" (a trade secret blend of 11 herbs and spices according to the can) - it was that or assume it was polymer resin and used polymer-based paint. I stand by my decision - plus epoxy paint is a little more resistant to solvents and chemicals.
I'll install it tomorrow with some temporary foam insulation - then we wait for China to do it's part.
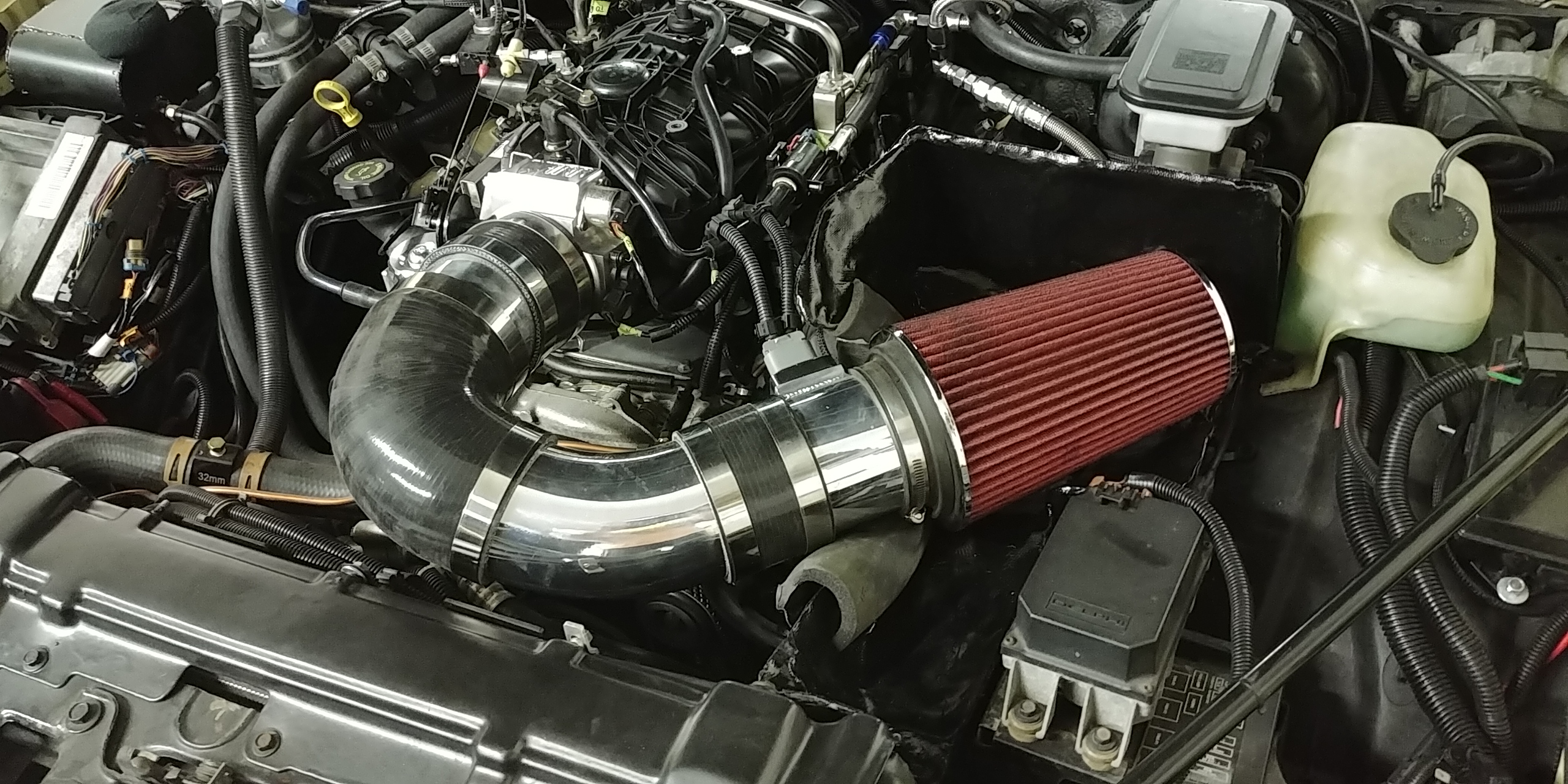
If you squint it doesn't look half bad with the hood closed.




P0106. Been chasing my *ss on this one for a while, finally found some information:
https://ls1tech.com/forums/pcm-diagnostics-tuning/139811-setting-p0106-map-performance.html
Long and skinny of it? Big cam problems.
Now if it isn't a tune issue?
DTC P0106
Circuit Description
The manifold absolute pressure (MAP) sensor responds to pressure changes in the intake manifold. The pressure changes occur based on the engine load. The MAP sensor has the following circuits:
A 5-volt reference circuit
A low reference circuit
A MAP sensor signal circuit
The powertrain control module (PCM) supplies 5 volts to the MAP sensor on the 5-volt reference circuit. The PCM, also, provides a ground on the low reference circuit. The MAP sensor provides a signal to the PCM on the MAP sensor signal circuit which is relative to the pressure changes in the manifold. The PCM should detect a low signal voltage at a low MAP, such as during an idle or a deceleration. The PCM should detect a high signal voltage at a high MAP, such as the ignition is ON, with the engine OFF, or at a wide-open throttle (WOT). The MAP sensor is also used in order to determine the barometric pressure (BARO). This occurs when the ignition switch is turned ON, with the engine OFF. The BARO reading may also be updated whenever the engine is operated at WOT. The PCM monitors the MAP sensor signal for voltage outside of the normal range.
The PCM calculates a predicted value for the MAP sensor based on throttle position (TP) and engine speed. The PCM then compares the predicted value to the actual MAP sensor signal. If the PCM detects that the MAP sensor signal is not within the predicted range, DTC P0106 sets.
Conditions for Running the DTC
DTC P0101, P0102, P0103, P0107, P0108, P0440, P0442, P0443, P0446, P1120, P1125, P1220, P1221, P1275, P1276, P1280, P1281, P1285, P1286, P1514, P1515, P1516, P1517, P1518 are not set.
The engine speed is between 400-5,000 RPM.
The change in engine speed is less than 125 RPM.
Traction control is not active.
The A/C compressor clutch is steady.
The power steering is stable.
The clutch switch state does not change.
The brake switch state does not change.
The above conditions are met for 1 second.
Conditions for Setting the DTC
The PCM detects that the MAP sensor voltage is not within the predicted range for 2 seconds.
Action Taken When the DTC Sets
The control module illuminates the malfunction indicator lamp (MIL) on the second consecutive ignition cycle that the diagnostic runs and fails.
The control module records the operating conditions at the time the diagnostic fails. The first time the diagnostic fails, the control module stores this information in the Failure Records. If the diagnostic reports a failure on the second consecutive ignition cycle, the control module records the operating conditions at the time of the failure. The control module writes the operating conditions to the Freeze Frame and updates the Failure Records.
Conditions for Clearing the MIL/DTC
The control module turns OFF the malfunction indicator lamp (MIL) after 3 consecutive ignition cycles that the diagnostic runs and does not fail.
A current DTC, Last Test Failed, clears when the diagnostic runs and passes.
A history DTC clears after 40 consecutive warm-up cycles, if no failures are reported by this or any other emission related diagnostic.
Clear the MIL and the DTC with a scan tool.
Test Description
The numbers below refer to the step numbers on the diagnostic table.
This step tests the ability of the MAP sensor to correctly indicate BARO.
This step tests the ability of the MAP sensor to respond to an increase in engine vacuum.
This step tests for a proper MAP sensor pressure with an applied vacuum.
Step
Action
Values
Yes
No
Schematic Reference: Engine Controls Schematics
Connector End View Reference: Powertrain Control Module (PCM) Connector End Views or Engine Controls Connector End Views
1
Did you perform the Diagnostic System Check-Engine Controls?
--
Go to Step 2
Go to Diagnostic System Check - Engine Controls
2
Inspect for the following conditions:
Vacuum hoses that are disconnected, damaged, or incorrectly routed
Manifold absolute pressure (MAP) sensor seal missing or damaged
Restrictions in the MAP sensor vacuum source
Intake manifold vacuum leaks
Did you find and correct the condition?
--
Go to Step 25
Go to Step 3
3
Important
The vehicle used for the comparison is not limited to the same type of vehicle as is being serviced. A vehicle known to provide an accurate reading is acceptable.
Do you have access to another vehicle in which the MAP sensor pressure can be observed with a scan tool?
--
Go to Step 4
Go to Step 5
4
Turn ON the ignition, with the engine OFF.
Observe the MAP sensor pressure with a scan tool.
Observe the MAP sensor pressure in the known good vehicle with a scan tool.
Compare the values.
Is the difference between the values less than the specified value?
3 kPa
Go to Step 6
Go to Step 11
5
Important
The Altitude vs. Barometric Pressure table indicates a pressure range for a given altitude under normal weather conditions. Weather conditions consisting of very low or very high pressure and/or very low or very high temperature may cause a reading to be slightly out of range.
Turn ON the ignition, with the engine OFF.
Observe the MAP sensor pressure with a scan tool. Refer to Altitude vs Barometric Pressure .
The MAP sensor pressure should be within the range specified for your altitude.
Does the MAP sensor indicate the correct barometric pressure?
--
Go to Step 6
Go to Step 11
6
Observe the MAP sensor pressure with a scan tool.
Start the engine.
Does the MAP sensor pressure change?
--
Go to Step 7
Go to Step 11
7
Turn OFF the ignition.
Remove the MAP sensor from the intake manifold. Refer to Manifold Absolute Pressure (MAP) Sensor Replacement . Leave the MAP sensor connected to the electrical harness.
Connect a J 23738-A Mityvac to the MAP sensor port.
Turn ON the ignition, with the engine OFF.
Observe the MAP sensor pressure with the scan tool.
Apply vacuum to the MAP sensor with the J 23738-A in 1 in Hg increments until 15 in Hg is reached. Each 1 in Hg should decrease MAP sensor pressure by 3-4 kPa.
Is the decrease in MAP sensor pressure consistent?
--
Go to Step 8
Go to Step 11
8
Observe the MAP sensor pressure with the scan tool.
Apply vacuum with the J 23738-A until 20 in Hg is reached.
Is the MAP sensor pressure less than the specified value?
34 kPa
Go to Step 9
Go to Step 11
9
Observe the MAP sensor pressure with the scan tool.
Disconnect the J 23738-A from the MAP sensor.
Does the MAP sensor pressure return to the original reading observed in Step 4 or Step 5?
--
Go to Step 10
Go to Step 23
10
Inspect for the following conditions:
Incorrect cam timing--Refer to Timing Chain and Sprockets Replacement in Engine Mechanical for the correct timing.
Restricted exhaust flow--Refer to Restricted Exhaust in Engine Exhaust.
Worn piston rings--Refer to Engine Compression Test in Engine Mechanical.
Did you find and correct the condition?
--
Go to Step 25
Go to Intermittent Conditions
11
Disconnect the MAP sensor electrical connector.
Observe the MAP sensor voltage with the scan tool.
Is the voltage less than the specified value?
0.1 V
Go to Step 12
Go to Step 16
12
Measure the voltage from the 5-volt reference circuit of the MAP sensor to a good ground with a DMM. Refer to Circuit Testing in Wiring Systems.
Is the voltage more than the specified value?
5.2 V
Go to Step 17
Go to Step 13
https://ls1tech.com/forums/pcm-diagnostics-tuning/139811-setting-p0106-map-performance.html
Long and skinny of it? Big cam problems.
Now if it isn't a tune issue?
DTC P0106
Circuit Description
The manifold absolute pressure (MAP) sensor responds to pressure changes in the intake manifold. The pressure changes occur based on the engine load. The MAP sensor has the following circuits:
A 5-volt reference circuit
A low reference circuit
A MAP sensor signal circuit
The powertrain control module (PCM) supplies 5 volts to the MAP sensor on the 5-volt reference circuit. The PCM, also, provides a ground on the low reference circuit. The MAP sensor provides a signal to the PCM on the MAP sensor signal circuit which is relative to the pressure changes in the manifold. The PCM should detect a low signal voltage at a low MAP, such as during an idle or a deceleration. The PCM should detect a high signal voltage at a high MAP, such as the ignition is ON, with the engine OFF, or at a wide-open throttle (WOT). The MAP sensor is also used in order to determine the barometric pressure (BARO). This occurs when the ignition switch is turned ON, with the engine OFF. The BARO reading may also be updated whenever the engine is operated at WOT. The PCM monitors the MAP sensor signal for voltage outside of the normal range.
The PCM calculates a predicted value for the MAP sensor based on throttle position (TP) and engine speed. The PCM then compares the predicted value to the actual MAP sensor signal. If the PCM detects that the MAP sensor signal is not within the predicted range, DTC P0106 sets.
Conditions for Running the DTC
DTC P0101, P0102, P0103, P0107, P0108, P0440, P0442, P0443, P0446, P1120, P1125, P1220, P1221, P1275, P1276, P1280, P1281, P1285, P1286, P1514, P1515, P1516, P1517, P1518 are not set.
The engine speed is between 400-5,000 RPM.
The change in engine speed is less than 125 RPM.
Traction control is not active.
The A/C compressor clutch is steady.
The power steering is stable.
The clutch switch state does not change.
The brake switch state does not change.
The above conditions are met for 1 second.
Conditions for Setting the DTC
The PCM detects that the MAP sensor voltage is not within the predicted range for 2 seconds.
Action Taken When the DTC Sets
The control module illuminates the malfunction indicator lamp (MIL) on the second consecutive ignition cycle that the diagnostic runs and fails.
The control module records the operating conditions at the time the diagnostic fails. The first time the diagnostic fails, the control module stores this information in the Failure Records. If the diagnostic reports a failure on the second consecutive ignition cycle, the control module records the operating conditions at the time of the failure. The control module writes the operating conditions to the Freeze Frame and updates the Failure Records.
Conditions for Clearing the MIL/DTC
The control module turns OFF the malfunction indicator lamp (MIL) after 3 consecutive ignition cycles that the diagnostic runs and does not fail.
A current DTC, Last Test Failed, clears when the diagnostic runs and passes.
A history DTC clears after 40 consecutive warm-up cycles, if no failures are reported by this or any other emission related diagnostic.
Clear the MIL and the DTC with a scan tool.
Test Description
The numbers below refer to the step numbers on the diagnostic table.
This step tests the ability of the MAP sensor to correctly indicate BARO.
This step tests the ability of the MAP sensor to respond to an increase in engine vacuum.
This step tests for a proper MAP sensor pressure with an applied vacuum.
Step
Action
Values
Yes
No
Schematic Reference: Engine Controls Schematics
Connector End View Reference: Powertrain Control Module (PCM) Connector End Views or Engine Controls Connector End Views
1
Did you perform the Diagnostic System Check-Engine Controls?
--
Go to Step 2
Go to Diagnostic System Check - Engine Controls
2
Inspect for the following conditions:
Vacuum hoses that are disconnected, damaged, or incorrectly routed
Manifold absolute pressure (MAP) sensor seal missing or damaged
Restrictions in the MAP sensor vacuum source
Intake manifold vacuum leaks
Did you find and correct the condition?
--
Go to Step 25
Go to Step 3
3
Important
The vehicle used for the comparison is not limited to the same type of vehicle as is being serviced. A vehicle known to provide an accurate reading is acceptable.
Do you have access to another vehicle in which the MAP sensor pressure can be observed with a scan tool?
--
Go to Step 4
Go to Step 5
4
Turn ON the ignition, with the engine OFF.
Observe the MAP sensor pressure with a scan tool.
Observe the MAP sensor pressure in the known good vehicle with a scan tool.
Compare the values.
Is the difference between the values less than the specified value?
3 kPa
Go to Step 6
Go to Step 11
5
Important
The Altitude vs. Barometric Pressure table indicates a pressure range for a given altitude under normal weather conditions. Weather conditions consisting of very low or very high pressure and/or very low or very high temperature may cause a reading to be slightly out of range.
Turn ON the ignition, with the engine OFF.
Observe the MAP sensor pressure with a scan tool. Refer to Altitude vs Barometric Pressure .
The MAP sensor pressure should be within the range specified for your altitude.
Does the MAP sensor indicate the correct barometric pressure?
--
Go to Step 6
Go to Step 11
6
Observe the MAP sensor pressure with a scan tool.
Start the engine.
Does the MAP sensor pressure change?
--
Go to Step 7
Go to Step 11
7
Turn OFF the ignition.
Remove the MAP sensor from the intake manifold. Refer to Manifold Absolute Pressure (MAP) Sensor Replacement . Leave the MAP sensor connected to the electrical harness.
Connect a J 23738-A Mityvac to the MAP sensor port.
Turn ON the ignition, with the engine OFF.
Observe the MAP sensor pressure with the scan tool.
Apply vacuum to the MAP sensor with the J 23738-A in 1 in Hg increments until 15 in Hg is reached. Each 1 in Hg should decrease MAP sensor pressure by 3-4 kPa.
Is the decrease in MAP sensor pressure consistent?
--
Go to Step 8
Go to Step 11
8
Observe the MAP sensor pressure with the scan tool.
Apply vacuum with the J 23738-A until 20 in Hg is reached.
Is the MAP sensor pressure less than the specified value?
34 kPa
Go to Step 9
Go to Step 11
9
Observe the MAP sensor pressure with the scan tool.
Disconnect the J 23738-A from the MAP sensor.
Does the MAP sensor pressure return to the original reading observed in Step 4 or Step 5?
--
Go to Step 10
Go to Step 23
10
Inspect for the following conditions:
Incorrect cam timing--Refer to Timing Chain and Sprockets Replacement in Engine Mechanical for the correct timing.
Restricted exhaust flow--Refer to Restricted Exhaust in Engine Exhaust.
Worn piston rings--Refer to Engine Compression Test in Engine Mechanical.
Did you find and correct the condition?
--
Go to Step 25
Go to Intermittent Conditions
11
Disconnect the MAP sensor electrical connector.
Observe the MAP sensor voltage with the scan tool.
Is the voltage less than the specified value?
0.1 V
Go to Step 12
Go to Step 16
12
Measure the voltage from the 5-volt reference circuit of the MAP sensor to a good ground with a DMM. Refer to Circuit Testing in Wiring Systems.
Is the voltage more than the specified value?
5.2 V
Go to Step 17
Go to Step 13
Cont'd...
13
Probe the 5-volt reference circuit of the MAP sensor with a test lamp that is connected to a good ground. Refer to Circuit Testing and Probing Electrical Connectors in Wiring Systems.
Is the test lamp OFF?
--
Go to Step 18
Go to Step 14
14
Connect a 3-amp fused jumper wire between the 5-volt reference circuit of the MAP sensor and the signal circuit of the MAP sensor.
Observe the MAP sensor voltage with the scan tool.
Is the voltage more than the specified value?
4.9 V
Go to Step 15
Go to Step 19
15
Turn OFF the ignition.
Remove the jumper wire.
Remove the MAP sensor form the intake manifold, unless the sensor was already removed in a previous step. Refer to Manifold Absolute Pressure (MAP) Sensor Replacement .
Connect a jumper wire between each of the terminals in the MAP sensor harness connector and the corresponding terminal at the MAP sensor. Refer to Using Connector Test Adapters in Wiring Systems.
Turn ON the ignition, with the engine OFF.
Measure the voltage from the low reference circuit of the MAP sensor at the jumper wire terminal to a good ground with a DMM. Refer to Measuring Voltage Drop in Wiring Systems.
Is the voltage more than the specified value?
0.2 V
Go to Step 20
Go to Step 21
16
Test the MAP sensor signal circuit between the PCM and the MAP sensor for a short to voltage. Refer to Circuit Testing and Wiring Repairs in Wiring Systems.
Did you find and correct the condition?
--
Go to Step 25
Go to Step 24
17
Test all of the branches of the 5-volt reference circuit that are shared with the MAP sensor for a short to voltage. Refer to Circuit Testing and Wiring Repairs in Wiring Systems.
Did you find and correct the condition?
--
Go to Step 25
Go to Step 24
18
Test the 5-volt reference circuit between the PCM and the MAP sensor for an open or for high resistance. Refer to Circuit Testing and Wiring Repairs in Wiring Systems.
Did you find and correct the condition?
--
Go to Step 25
Go to Step 22
19
Test the MAP sensor signal circuit between the PCM and the MAP sensor for the following conditions:
A short to ground
An open
A high resistance
Refer to Circuit Testing and Wiring Repairs in Wiring Systems.
Did you find and correct the condition?
--
Go to Step 25
Go to Step 22
20
Test the low reference circuit between the PCM and the MAP sensor for an open or for high resistance. Refer to Circuit Testing and Wiring Repairs in Wiring Systems.
Did you find and correct the condition?
--
Go to Step 25
Go to Step 22
21
Test for an intermittent and for a poor connection at the MAP sensor. Refer to Testing for Intermittent and Poor Connections and Connector Repairs in Wiring Systems.
Did you find and correct the condition?
--
Go to Step 25
Go to Step 23
22
Test for an intermittent and for a poor connection at the PCM. Refer to Testing for Intermittent and Poor Connections and Connector Repairs in Wiring Systems.
Did you find and correct the condition?
--
Go to Step 25
Go to Step 24
23
Replace the MAP sensor. Refer to Manifold Absolute Pressure (MAP) Sensor Replacement .
Did you complete the replacement?
--
Go to Step 25
--
24
Replace the PCM. Refer to Powertrain Control Module (PCM) Replacement .
Did you complete the replacement?
--
Go to Step 25
--
25
Clear the DTCs with a scan tool.
Turn OFF the ignition for 30 seconds.
Start the engine.
Operate the vehicle within the conditions for running the DTC. You may also operate the vehicle within the conditions that you observed from the Freeze Frame/Failure Records.
Did the DTC fail this ignition?
--
Go to Step 2
Go to Step 26
26
Observe the Capture Info with a scan tool.
Are there any DTCs that have not been diagnosed?
--
Go to Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) List
System OK
13
Probe the 5-volt reference circuit of the MAP sensor with a test lamp that is connected to a good ground. Refer to Circuit Testing and Probing Electrical Connectors in Wiring Systems.
Is the test lamp OFF?
--
Go to Step 18
Go to Step 14
14
Connect a 3-amp fused jumper wire between the 5-volt reference circuit of the MAP sensor and the signal circuit of the MAP sensor.
Observe the MAP sensor voltage with the scan tool.
Is the voltage more than the specified value?
4.9 V
Go to Step 15
Go to Step 19
15
Turn OFF the ignition.
Remove the jumper wire.
Remove the MAP sensor form the intake manifold, unless the sensor was already removed in a previous step. Refer to Manifold Absolute Pressure (MAP) Sensor Replacement .
Connect a jumper wire between each of the terminals in the MAP sensor harness connector and the corresponding terminal at the MAP sensor. Refer to Using Connector Test Adapters in Wiring Systems.
Turn ON the ignition, with the engine OFF.
Measure the voltage from the low reference circuit of the MAP sensor at the jumper wire terminal to a good ground with a DMM. Refer to Measuring Voltage Drop in Wiring Systems.
Is the voltage more than the specified value?
0.2 V
Go to Step 20
Go to Step 21
16
Test the MAP sensor signal circuit between the PCM and the MAP sensor for a short to voltage. Refer to Circuit Testing and Wiring Repairs in Wiring Systems.
Did you find and correct the condition?
--
Go to Step 25
Go to Step 24
17
Test all of the branches of the 5-volt reference circuit that are shared with the MAP sensor for a short to voltage. Refer to Circuit Testing and Wiring Repairs in Wiring Systems.
Did you find and correct the condition?
--
Go to Step 25
Go to Step 24
18
Test the 5-volt reference circuit between the PCM and the MAP sensor for an open or for high resistance. Refer to Circuit Testing and Wiring Repairs in Wiring Systems.
Did you find and correct the condition?
--
Go to Step 25
Go to Step 22
19
Test the MAP sensor signal circuit between the PCM and the MAP sensor for the following conditions:
A short to ground
An open
A high resistance
Refer to Circuit Testing and Wiring Repairs in Wiring Systems.
Did you find and correct the condition?
--
Go to Step 25
Go to Step 22
20
Test the low reference circuit between the PCM and the MAP sensor for an open or for high resistance. Refer to Circuit Testing and Wiring Repairs in Wiring Systems.
Did you find and correct the condition?
--
Go to Step 25
Go to Step 22
21
Test for an intermittent and for a poor connection at the MAP sensor. Refer to Testing for Intermittent and Poor Connections and Connector Repairs in Wiring Systems.
Did you find and correct the condition?
--
Go to Step 25
Go to Step 23
22
Test for an intermittent and for a poor connection at the PCM. Refer to Testing for Intermittent and Poor Connections and Connector Repairs in Wiring Systems.
Did you find and correct the condition?
--
Go to Step 25
Go to Step 24
23
Replace the MAP sensor. Refer to Manifold Absolute Pressure (MAP) Sensor Replacement .
Did you complete the replacement?
--
Go to Step 25
--
24
Replace the PCM. Refer to Powertrain Control Module (PCM) Replacement .
Did you complete the replacement?
--
Go to Step 25
--
25
Clear the DTCs with a scan tool.
Turn OFF the ignition for 30 seconds.
Start the engine.
Operate the vehicle within the conditions for running the DTC. You may also operate the vehicle within the conditions that you observed from the Freeze Frame/Failure Records.
Did the DTC fail this ignition?
--
Go to Step 2
Go to Step 26
26
Observe the Capture Info with a scan tool.
Are there any DTCs that have not been diagnosed?
--
Go to Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) List
System OK
Ugh.
I think I’m gonna stay stuck in the Stone Age with my carburetor.
I think I’m gonna stay stuck in the Stone Age with my carburetor.
I guess it's safe to assume that the PCM's "prediction" cannot be manipulated by HPT?
I guess it's safe to assume that the PCM's "prediction" cannot be manipulated by HPT?
Au contraire mon frère !
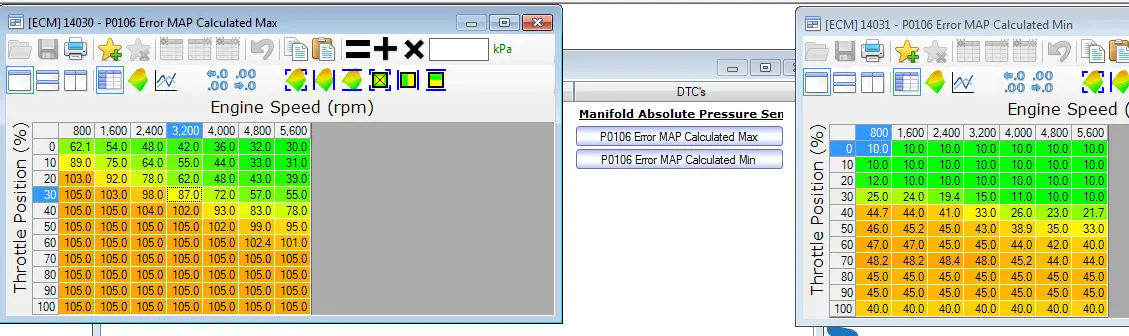
Basically just up the limits between 0-20% throttle position and 800 to 3200rpm by about 2.5 to 10% for the Calculated Max and that should stop it from tripping the code.
- Status
- Not open for further replies.
Similar threads
- Replies
- 2
- Views
- 895
- Replies
- 3
- Views
- 231
GBodyForum is a participant in the Amazon Services LLC Associates Program, an affiliate advertising program designed to provide a means for sites to earn advertising fees by advertising and linking to amazon.com. Amazon, the Amazon logo, AmazonSupply, and the AmazonSupply logo are trademarks of Amazon.com, Inc. or its affiliates.

